Empower Your
Online Presence
Your website is the face of your business. That’s why we work with you to create a website that looks great and delivers results.
Whether you need a simple business website or a complex e-commerce platform, our team of experts has the skills and experience to make it happen.
Our Services
Achieve Your Digital Goals with a Results-Driven Agency
WordPress Website Development
Get a stunning, responsive website that reflects your brand’s vision and enhances your online presence using the latest WordPress technology
Shopify Store Development
We will build a fully customizable and user-friendly e-commerce store that drives conversions and takes your online business to the next level.
Custom Website Development
Get a personalized website that’s built specifically for your business needs. We’ll ensure your website is fast, secure, responsive, and looks great.
Website Redesigning
Transform your outdated website into a modern, visually stunning platform that attracts, engages, and converts your target audience.
SEO/SEM
Boost your online visibility, traffic, and conversions through targeted search engine optimization and marketing campaigns that drive results.
SMM
Connect with your audience and increase brand awareness through strategic social media marketing that drives engagement, shares, and growth.
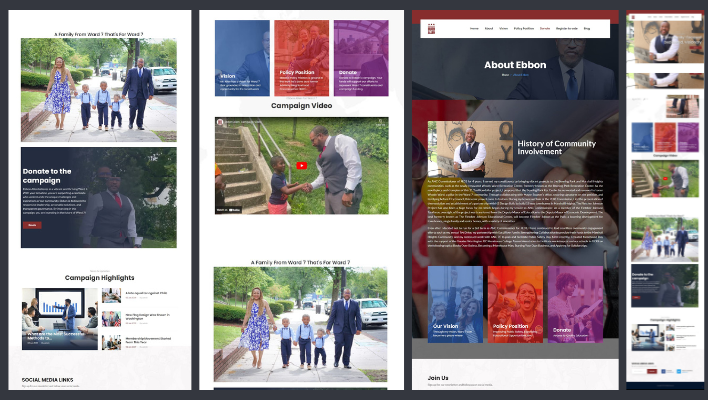
Our Portfolio
Explore Our Impressive Work
Empowering Clients Like You to Surpass Their Goals
See what our clients have to say about us.

Swattik Chakraborty
Founder & CEO
SS Bamboowala Pvt Ltd
“This was my first experience of hiring a freelancer from UpWork and, not only Munendra established himself as a FANTASTIC FREELANCER in this Domain; he also established, UpWork is an awesome platform to get works done.
Munendra’s Service is highly advised for anyone & everyone who is struggling to get website up & running.
He precisely and successfully Created Main Corporate Website of Our Business and Password Protected Catalog Site and all these within a time frame of 10 Days. Extremely Friendly & Professional to work with, and has the ability to work as a Team member.
In future, If I have to hire any freelancer for Web Design & Development Jobs, he will be my first choice.
Well Done Munendra! YOU DID A FANTASTIC JOB! Best Wishes for Future Endeavors!”

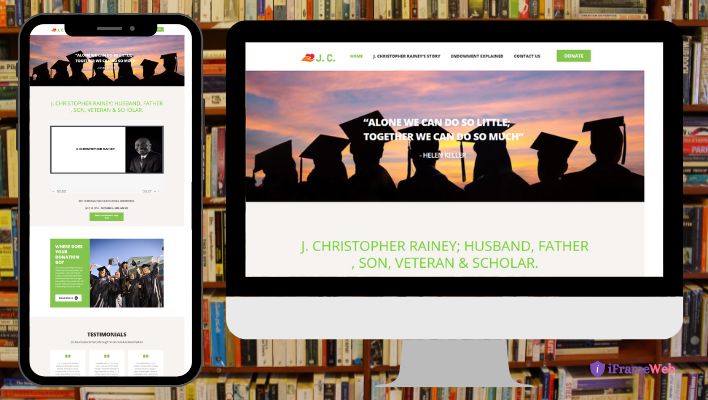
Frederick V. Gill
Site Administrator
JCRaineyEndowment
“This developer is phenomenal! Despite the distance, time zones, and near daily updates from me, he always remained accessible and responsive.
This project held special significance for me. My dear friend was injured as a result of a surgery and he has been left in a terrible state. The developer was very compassionate and it is obvious that his final product took this into consideration.
I have already commissioned him for two more projects and I highly recommend his services….
HE IS SIMPLY SUPERB!!!!! Thanks again for your dedication and hard work on this project….we really appreciate your efforts.”

Dmytro Baranov
Manager
Traffic Timer Ltd
“I was really glad to work with Munendra. The work was done really quality and fast. All the requirements and deadlines were fully met. In addition, he’s polite and very hardworking. I strongly recommend to cooperate with Munendra”